Nucleosides
apps進(jìn)入產(chǎn)品列表
General structures for Nucleosides
Nucleosides are glycosylamines that can be thought of as nucleotides without a phosphate group. A nucleoside consists simply of a nucleobase (also termed a nitrogenous base) and a five-carbon sugar (either ribose or deoxyribose), whereas a nucleotide is composed of a nucleobase, a five-carbon sugar, and one or more phosphate groups. In a nucleoside, the anomeric carbon is linked through a glycosidic bond to the N9 of a purine or the N1 of a pyrimidine. Examples of nucleosides include cytidine, uridine, adenosine, guanosine, thymidine and inosine.
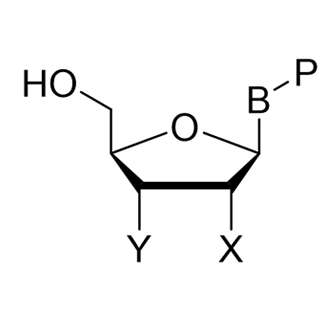
B = Base (A, C, G, U, T, I, X, pU, iso-C, iso-G)
P = Null, Me, F, Cl, Br, I, NH2, isotope, deaza, thio, etc.
X/Y = H, OH, F, OTBDMS, OMe, OMOE, O-Propargyl,
NH2, N3, etc.
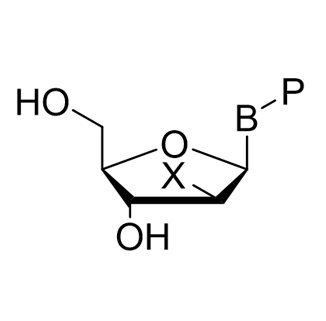
B = Base (A, C, G, U, I, T)
P = Null, Me, F, NH2, etc.
X = OH, F
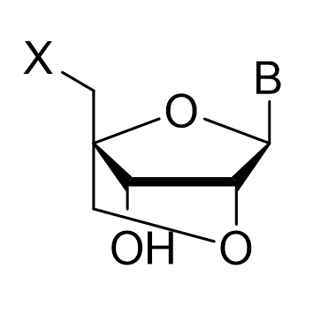
B = Base (A, C, G, U, T, etc)
X = OH, NH2, etc.


